
In a realm often unseen by the average individual, personal details are meticulously gathered and exchanged. Many people remain blissfully unaware of how their online presence is commodified. Every click, every search, and every purchase creates a digital footprint. This footprint becomes a part of a complex web, where various entities engage in a silent dance of acquisition and sale.
These operations operate behind a curtain of ambiguity, where anonymity reigns supreme. Vast networks compile profiles that range from basic preferences to intricate behavioral patterns. This hidden economy flourishes largely unnoticed, feeding on the very essence of modern digital life. Unbeknownst to users, their data is continuously collected, analyzed, and packaged for a variety of purposes.
As you delve deeper, a complex narrative unfolds, revealing the intricate relationships that exist between collectors and consumers of these profiles. Transactions happen in real-time; profiles are adjusted, updated, and sold to the highest bidder. For many, this is merely a business practice, but for others, it raises crucial questions about privacy and consent.
The implications of such practices extend far beyond mere marketing strategies, touching on issues of personal agency and surveillance. With the rise of technology, the boundaries of what is acceptable are constantly shifting. Are individuals truly aware of the extent to which their lives are mapped, recorded, and sold? The intricate dynamics of this exchange challenge our understanding of privacy in the digital age.
Ultimately, shedding light on this murky trade is essential for fostering informed conversations about privacy rights and responsibilities. Understanding the mechanics behind these exchanges can empower users, equipping them with the knowledge needed to navigate their digital existence more consciously. The journey into this hidden sector reveals not just the practices at play, but also the broader implications for society at large.
Understanding the Role of Data Brokers

In the complex and often opaque ecosystem of personal information management, certain entities play pivotal roles. They thrive in the shadows, capitalizing on the immense value of the personal details shared by individuals. These organizations aggregate, analyze, and resell data, often without the direct consent of those whose information is being utilized. It’s a service that many may not even be aware exists.
But how do they operate in this ambiguous landscape?
- Collection of data from various sources
- Aggregation of information into comprehensive profiles
- Analysis to determine patterns and trends
- Distribution of insights to interested parties
These entities often start by gathering information from public records, social media, online transactions, and even surveys. They then combine this data to create extensive profiles that reflect the behaviors, preferences, and even the potential future actions of individuals. The true extent of this operation can be staggering, revealing insights that go beyond simple demographics.
For example, a single profile might include details about a person’s financial status, shopping habits, and online behavior, piecing together a comprehensive picture that businesses can use for targeted advertising. This means that a consumer’s data can be sold to advertisers or other companies looking to tailor their marketing strategies.
The process is methodical, driven by algorithms and trends that help these entities understand and predict consumer behavior. As such, they often operate in secrecy, leaving many people unaware of how their information is being compiled and used.
- The collection process is often automated and extensive.
- They utilize advanced algorithms for data analysis.
- Transparency is minimal, leading to trust issues.
- The impact of their work is felt across numerous industries.
While many might perceive these practices as a harmless business model, the implications for personal privacy are significant. As a result, the lack of awareness and understanding about how these organizations operate can lead to unsettling consequences for individuals.
How Data Brokers Operate in Secrecy
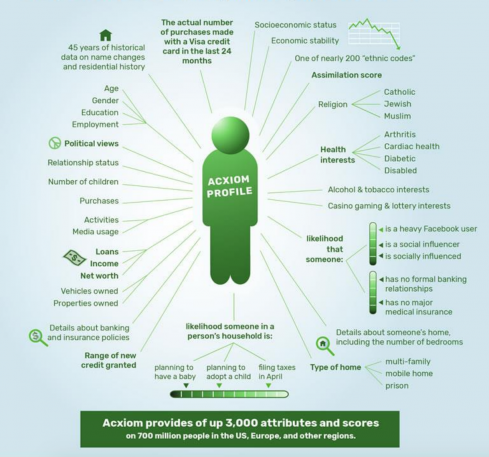
Every day, a vast network silently spins, weaving together countless threads of personal details. Many remain unaware of this intricate web. The exchange of private facts happens behind closed doors. Individuals may not realize how their information is gathered and utilized. The obscurity surrounding these operations raises numerous questions about ethics and responsibility.
While most people value their privacy, they often overlook how easily it can be compromised. Information gathering takes many forms and is facilitated by various techniques. Online footprints, purchase histories, and social media interactions are just click the following article a few treasures collected by this clandestine industry. Companies compile, analyze, and sell these details without drawing much attention.
Transacting in personal data is done discreetly, often shielded from public scrutiny. Many transactions occur through specialized platforms where anonymity is the norm. Here, a plethora of entities engage in complex partnerships to maximize profit while minimizing exposure. In essence, the entire system thrives on a lack of transparency.
Privacy violations can have profound implications, affecting everything from financial stability to social standing. Yet, evaluating the risks is challenging when the process remains shrouded in secrecy. Users typically consent to policies without fully comprehending the ramifications of their decisions. This ignorance perpetuates a cycle of exploitation, allowing the industry to flourish undeterred.
| Concerns | Implications |
|---|---|
| Invasion of privacy | Loss of personal autonomy |
| Manipulation of data | Distorted public perceptions |
| Lack of transparency | Increased distrust in platforms |
| Regulatory loopholes | Continued exploitation of consumers |
The future concerns surrounding privacy in this context cannot be understated. As more people become aware of their sensitive information being exploited, a growing demand for accountability and transparency will likely arise. Individuals may begin to advocate for stricter regulations designed to protect their rights. Such movements can fundamentally reshape the landscape, urging businesses to prioritize ethical practices and prioritize consumer trust.
The Impact of Data Trading on Privacy

The exchange of personal information has profound implications for individual privacy. As entities increasingly gather and sell consumer details, questions surrounding consent and ethical usage arise. Individuals often remain unaware of how their data is collected or utilized. The very foundation of privacy begins to erode when personal information is commodified.
Every transaction creates a ripple effect. Once released, personal insights can spread rapidly across various platforms, often beyond the original user’s control. Each click, purchase, or social interaction provides fodder for entities eager to capitalize on consumer behavior. This commodification not only undermines the concept of privacy but also leads to significant anxiety among individuals regarding their unique identities.
Individuals find themselves tangled in a web of surveillance and data collection. Many feel a growing sense of vulnerability. The constant monitoring has become a part of everyday life. Consumers often question whether they still possess autonomy over their own information. This manipulation fosters distrust, not just towards corporations, but also within interpersonal relationships.
Moreover, when personal information is aggregated, it can lead to profiling and discrimination. Such practices may result in unfair treatment in various aspects of life, such as employment opportunities or credit access. These consequences underline the urgency for stronger safeguards and transparent practices to protect users from exploitation.
As new technologies emerge, the conflict between privacy rights and commercial gain intensifies. The landscape is not just about ethical concerns; it’s about building resilience against possible misuse. Individuals deserve clarity regarding who accesses their information and for what purposes. Ultimately, fostering greater awareness can empower consumers to regain control over their personal narratives.
Key Players in the Information Marketplace
The landscape of personal data and privacy is shaped by various significant entities that operate behind the scenes. These players navigate a complex ecosystem, contributing to the flow of information and influencing consumer experience. They range from large corporations to smaller, specialized firms, each with unique approaches and strategies. Understanding their roles is crucial to grasp the nuances of this industry, which often operates with greater secrecy than one might assume.
Many of these entities analyze user behavior, gathering data from multiple sources. They sell insights and profiles that can target specific audiences. This practice creates a web of interconnected networks, where personal information is commodified and traded. Moreover, the vast amount of data collected allows these players to make predictive analyses that can greatly impact marketing initiatives, product development, and even political campaigns.
In this ecosystem, some organizations act as aggregators, collecting and synthesizing information from a variety of channels. Others delve into niche markets, focusing on specific demographics or interests. The methods employed vary widely; some use ethical approaches, while others may operate on the periphery of legal boundaries.
Industry giants like tech companies and social networks play a dominant role, leveraging their vast user bases to compile extensive databases. Their influence extends beyond mere collection; they shape regulations, consumer expectations, and even public discourse. Smaller firms, on the other hand, often specialize in specific niches, offering tailored services and insights. Each participant in this marketplace has a different objective, which contributes to the overall complexity of the information landscape.
However, the practices of these organizations raise ethical concerns. Misleading information can easily proliferate, leading to significant consequences for consumers and businesses alike. As various entities vie for market share, the pressure to manipulate or oversell data becomes more pronounced. Additionally, the public’s trust in these players is often shaken by scandals and breaches of privacy, creating a climate of skepticism.
As scrutiny of their practices increases, it becomes essential for these organizations to navigate the regulatory environment carefully. Many are finding themselves at a crossroads, needing to balance innovation with responsibility. The implications of their actions ripple through society, highlighting the intricate dance between commerce and ethics in a digital age marked by constant connectivity.
Misinformation and Data Broker Practices
In today’s digital landscape, the exchange of personal details has become a complex and often opaque process. The nuances of this environment give rise to numerous challenges, particularly related to accuracy and trustworthiness. Sources may distort the truth or present information in misleading ways. As a result, consumers frequently find themselves in a maze of conflicting narratives and incomplete truths. Misinformation can lead to severe consequences for individuals and organizations alike.
One significant area that raises concern is how entities gather and utilize personal insights. Many lack transparency in their operations, making it difficult for individuals to discern where their information is sourced. Sometimes, practices can involve exaggerating the value or reliability of certain insights. This can foster a culture of mistrust, where users question the integrity of the data they receive.
Furthermore, the interplay between privacy settings and data collection often leads to confusion. Users might believe their preferences are respected, only to discover later that their details are shared beyond expected boundaries. This disconnect can result in an erosion of confidence in digital platforms.
Regulatory bodies face significant hurdles in addressing these challenges. The rapid innovation in technology outpaces the slow-moving legislative processes. Enforcing compliance becomes increasingly complicated, especially when dealing with diverse regions and jurisdictions. Consequently, many unscrupulous actors exploit these gaps, perpetuating cycles of misinformation.
| Challenge | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Lack of Transparency | Increased Mistrust Among Users |
| Misleading Practices | Inflated Value of Personal Insights |
| Slow Regulatory Response | Exploitation by Unscrupulous Actors |
| Confusing Privacy Settings | Loss of Confidence in Digital Platforms |
Ultimately, consumers are caught in a tug-of-war between their desire for personalization and their need for privacy assurance. The ramifications of questionable practices extend beyond individual experiences, shaping the very foundations of trust in the digital economy. Ongoing dialogue and greater awareness are essential to navigate this intricate web of relationships and to advocate for more ethical standards in this evolving space.
Regulatory Challenges Facing the Industry
The landscape of personal information exchange is fraught with complexities. One of the most pressing issues revolves around governance and oversight. As technology advances, so too do the methods of gathering and distributing personal details. Consequently, creating effective regulations becomes increasingly challenging. The distinction between ethical practices and exploitation often blurs in this evolving marketplace.
Authorities struggle to keep pace with rapid innovations. Many consumers remain unaware of how their private information is utilized. This lack of transparency exacerbates concerns about privacy violations. Moreover, regulatory bodies face immense pressure to enact protective measures that are both comprehensive and adaptable.
With each passing year, new technologies emerge that complicate regulation even further. For instance, artificial intelligence and machine learning tools enhance the capability to analyze vast amounts of personal data. While these advancements can bring about improved services, they also raise red flags about the ethical implications and potential misuse.
Furthermore, collaborations across borders pose significant hurdles. Different jurisdictions have varying laws concerning privacy, creating a patchwork of regulations that can confuse companies and consumers alike. This disjointed framework makes it difficult for agencies to enforce compliance consistently, which in turn undermines the effectiveness of any protective measures that may be in place.
Several groups advocate for stronger standards, emphasizing the necessity for transparency. They argue that individuals should possess the right to know who has access to their private information and how it is being leveraged. This push for clarity highlights an ongoing tension between economic interests and consumer rights. The debate continues, with no clear resolution in sight.
As discussions surrounding privacy and regulation intensify, stakeholders await potential legislative reforms. Revisions to existing laws would ideally reflect not only current realities but also anticipate future developments. However, achieving consensus on what those regulations should entail remains an uphill battle.
In the end, the quest for balanced oversight is crucial. Striking a harmony between innovation and privacy protection is essential for fostering public trust. Without it, the relationship between individuals and entities that handle their information could suffer irreparable damage.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage
The realm of personal information exchange is rapidly evolving. As technology advances, so do the methodologies employed in this industry. Consumers are becoming more aware, and their expectations are changing. Increasingly, transparency and ethical practices are at the forefront of discussions.
Companies are now exploring new ways to collect and utilize personal details while balancing privacy concerns. For instance, the rise of artificial intelligence has introduced innovative approaches to data analysis. Enhanced analytics tools enable organizations to gather insights more efficiently. However, such advancements bring new ethical dilemmas that must be addressed.
As regulations tighten globally, firms may have to adapt or risk penalties. New laws are emerging, focusing on consumer rights and how data is managed. In Europe, for example, stricter guidelines are already shaping operational practices. It’s clear that compliance will become a significant aspect of future operations.
Moreover, the demand for consent-driven models is on the rise. Users want control over how their personal information is used. This shift may lead to a broader adoption of opt-in frameworks. These allow individuals to give explicit permission before any information sharing occurs.
Table 1: Expected Trends in Personal Data Exchange
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Transparency | Organizations will provide clearer information on data usage. |
| Stronger Regulations | New laws will enforce stricter compliance and consumer rights. |
| AI Integration | Artificial intelligence will optimize data analysis processes. |
| Consent-Driven Models | Opt-in frameworks will gain popularity among consumers. |
In addition to these developments, consumer trust is becoming essential for business sustainability. Companies that prioritize ethical practices will likely thrive in this competitive landscape. Organizations that overlook these trends may find themselves facing backlash. As consumers become more discerning, safeguarding trust will be a critical factor for success.
Lastly, technological advancements promise further changes ahead. Blockchain technology, for instance, offers potential solutions for secure data sharing. By ensuring the integrity of transactions, it can bolster user confidence significantly. The future will see a merging of innovation with ethical considerations, fundamentally redefining how information is handled.
